Table of Contents
An Overview of Different Types of Lithium Batteries
Our world has changed dramatically because of lithium batteries, which power everything from electric cars to cell phones. However, there are a variety of choices available in the lithium market, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
In this blog, Renovar helps you to explore the six most prevalent types of lithium batteries.
Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO)
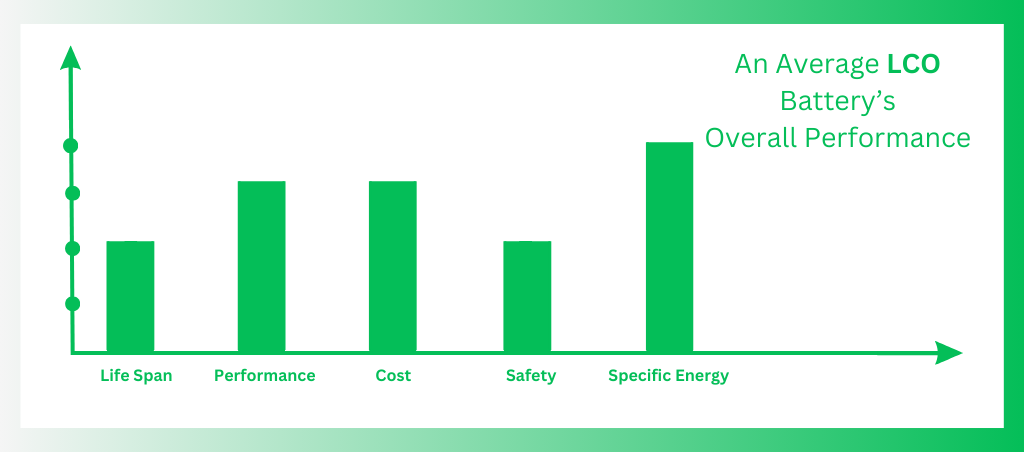
LiCoO2 cells have a low specific power but a high specific energy. This indicates that although they can supply electricity for an extended amount of time, they do not function effectively in high-load situations.
Characteristics of LCO
| Cycle Life | 500 – 1000 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 0.7–1C to 4.20V (3h typical); avoid >1C. Turn off when the current saturates at 0.05C. |
| Discharge Rate | Maintain 1C; cutoff at 2.50V. Avoid >1C for prolonged battery life. |
| Voltages | Nominal: 3.60 V; Operating range: 3.0 – 4.2 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 150 – 200 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- High energy density (stores a lot of energy in a small space)
- Long lifespan (can undergo many charge/discharge cycles)
Drawbacks
- Expensive
- Less stable (can overheat in extreme conditions)
- Contains cobalt, raising ethical and environmental concerns
LCO – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Early laptops and mobile phones (being phased out due to drawbacks)
Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
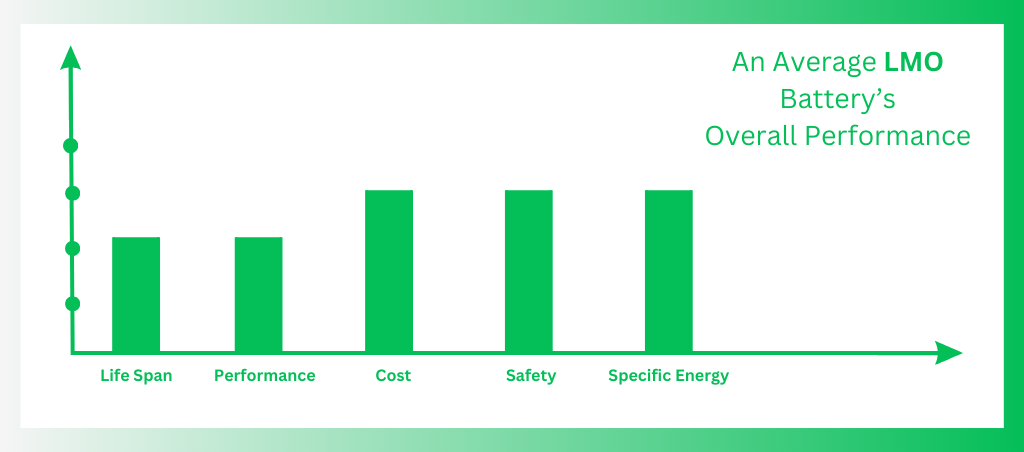
Lithium manganese oxide is used as the cathode material in LiMn2O4 batteries. This chemical produces a three-dimensional structure that enhances thermal stability and safety, boosts current handling, decreases internal resistance and improves ion movement.
Characteristics of LMO
| Cycle Life | 300 – 700 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 0.7–1C (3C max), up to 4.20V. Turn off at 0.05C saturation. |
| Discharge Rate | 1C (up to 10C, 30C pulse for 5s), cutoff at 2.50V. |
| Voltages | Nominal: 3.70 V; Operating range: 3.0 – 4.2 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 100 – 150 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- Good safety characteristics
- Stable at high temperatures
Drawbacks
- Lower energy density compared to LCO and NMC
- Shorter lifespan
LMO – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Power tools
- Medical devices
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
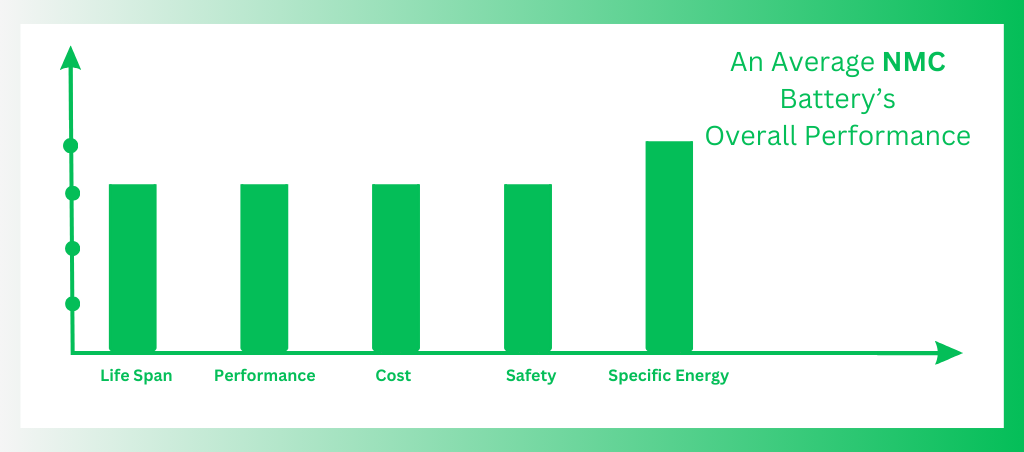
The advantages of nickel, manganese, and cobalt – the three primary elements utilised in the cathode – are combined in LiNiMnCoO2 batteries.
Although nickel has a high specific energy on its own, it is not stable. Manganese has a low specific energy but is remarkably stable. A stable chemical with a high specific energy is produced when they are combined.
Characteristics of NMC
| Cycle Life | 1000 – 2000 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 0.7–1C to 4.20V (some to 4.30V); 3h typical. Avoid >1C for longer life. Turn off at 0.05C saturation. |
| Discharge Rate | 1C (2C possible on some); cutoff at 2.50V. |
| Voltages | Nominal: 3.70 V; Operating range: 3.0 – 4.2 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 150 – 220 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- High energy density (longer driving range for EVs)
- Good overall performance
Drawbacks
- Less safe compared to LFP
- Shorter lifespan than LFP
- More expensive than LFP
NMC – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Electric vehicles (especially high-performance models)
- Power tools
Note: To learn about safer battery disposal, click here!
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
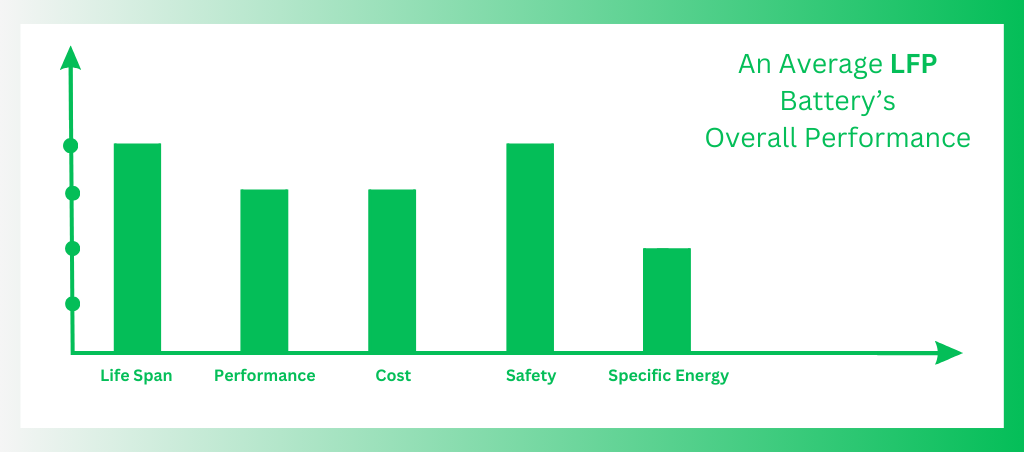
Phosphate serves as the cathode material in LiFePO4 batteries, while graphitic carbon electrodes serve as the anode. Long-lasting LFP batteries provide strong temperature stability and electrochemical performance.
Characteristics of LFP
| Cycle Life | 2000 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 1C to 3.65V, 3h typical; turn off at 0.05C saturation. |
| Discharge Rate | 1C (25C possible on some); 40A pulse for 2s; cutoff at 2.50V (avoid <2V to prevent damage). |
| Voltages | Nominal: 3.30 V; Operating range: 2.5 – 3.65 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 90 – 120 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- Excellent safety (most stable lithium chemistry)
- Long lifespan (can last for thousands of cycles)
- Affordable
Drawbacks
- Lower energy density compared to NMC and NCA
- Slower charging compared to some other lithium batteries
LFP – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Electric vehicles (especially focusing on safety and durability)
- Energy storage systems
Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
LiNiCoAlO2 batteries have a long lifespan, good specific energy, and reasonable specific power. Thus, they have a long-term capacity to deliver a sizable amount of current.
Characteristics of NCA
| Cycle Life | 500 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 0.7C to 4.20V (3h typical); fast charge with some cells. Turn off at 0.05C saturation. |
| Discharge Rate | 1C; cutoff at 3.00V. High discharge shortens battery life. |
| Voltages | Nominal: 3.60 V; Operating range: 3.0 – 4.2 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 200 – 260 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- High energy density (similar to NMC)
- Good power output
Drawbacks
- Less safe compared to LFP
- Similar drawbacks to NMC regarding stability and cost
NCA – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Electric vehicles (especially high-performance models)
- Power tools
Lithium Titanate (LTO)
The cathode material’s chemical composition distinguishes each of the earlier lithium battery types we covered. Li2TiO3 batteries employ LMO or NMC as the cathode chemistry and substitute lithium titanate for graphite in the anode.
The end product is a long-lasting, incredibly safe battery that charges faster than any other lithium battery.
Characteristics of LTO
| Cycle Life | 3,000 – 7,000 cycles |
| Charge Rate | 1C (5C max) to 2.85V; turn off at 0.05C saturation. |
| Discharge Rate | 10C (30C 5s pulse); cutoff at 1.80V for LCO/LTO. |
| Voltages | Nominal: 2.40 V; Operating range: 1.8 – 2.85 V/cell |
| Specific Energy | 50 – 80 Wh/kg |
Source: Battery University
Benefits
- Extremely long lifespan (up to 20,000 cycles)
- Excellent safety
- Fast charging
Drawbacks
- Very low energy density (limited range for EVs)
LTO – Types of Lithium Batteries
Applications
- Public transport buses (due to long lifespan and fast charging)
- Power tools requiring frequent charging
Summing Up
The world of lithium batteries offers a variety of options, each catering to specific needs. While LCO offers high energy density, its safety concerns and ethical considerations limit its application.
LFP, on the other hand, prioritises safety and lifespan, making it ideal for applications like electric vehicles prioritising durability.
Ultimately, the choice of the right battery depends on the specific requirements for power, safety, and cost.
Renovar, your battery recycling partner, specialise in lithium ion batteries recycling. If you are an EV owner, Make sure you contact us for eco-friendly recycling. Get fair compensation for your old batteries!
FAQ
What types of lithium batteries used in electric vehicles?
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM) and lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxide (NCA) are commonly used in EVs.
Are there different types of lithium batteries?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries come in various types, such as Li-cobalt oxide (LCO), Li-manganese oxide (LMO) and Li-titanate oxide (LTO), each with unique characteristics.
What are the types of rechargeable lithium batteries?
Common rechargeable lithium batteries include lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries.
Which is the best type of lithium battery?
The choice depends on the application. LiFePO4 is known for safety for electric vehicles, while NMC offers a balance of energy density and performance.
Which type of battery is better for a power bank: lithium-ion or lithium-polymer?
Both lithium-ion and lithium-polymer are suitable for power banks. Lithium-ion may offer higher energy density, while lithium polymer provides flexibility in design.
What types of lithium-ion batteries are used in cars?
Electric cars often use different types of lithium batteries, with variations like NCM and NCA, providing a balance of energy density and power.
What type of battery is lithium?
Lithium is used in rechargeable batteries, particularly in lithium-ion and lithium polymer types.
What type of electrolyte is used in lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries commonly use a liquid electrolyte, which is a solution containing lithium salts. Solid-state electrolytes are also being researched for future advancements.


