Table of Contents
FAQs on Lithium-Ion Batteries
If you ask an AI, what is the future of transportation? The first thing it lists is EVs. Let’s just say EV is the truth. The next question that comes to your mind is: What is EVs power source? The answer is Li-ion Batteries.
You can ask, what is the purpose of this blog? It is Renovar’s effort to educate you about the power source of the future of transportation.
What is a lithium-ion battery?
In general, a Li-ion battery is an electrochemical device. It stores and delivers electrical energy.
Technical Data of Lithium
| Common Name | Lithium |
| Symbol | Li |
| Atomic Weight | 6.94 |
| Atomic Number | 3 |
| Density | 0.535 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1342 °C |
| Melting Point | 180.54 °C |
For complete technical data, click here.
What is an Ion?
An atom or molecule with a positive/negative charge of a certain magnitude.
How do lithium-ion batteries work?
Li-ion batteries consist of 6 major components they are electrolyte, anode, cathode, separator and positive & negative collector.
Let’s discuss the purpose of each component. It helps us to understand better.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Anode | Stores Li & releases Li-ion when the battery is discharging. |
| Cathode | Stores Li & releases Li-ion when the battery is charging. |
| Separator | Permits Li-ions to go from the anode to the cathode & vice versa. Prevents electrons from flowing inside the battery. |
| Electrolyte | A liquid medium by which Li-ions move. |
| Positive Current Collector | Receives electrons from the negative current collector through the external circuit while discharging. |
| Negative Current Collector | Receives electrons from the positive current collector through the external circuit while charging. |
Process of Charge & Discharge
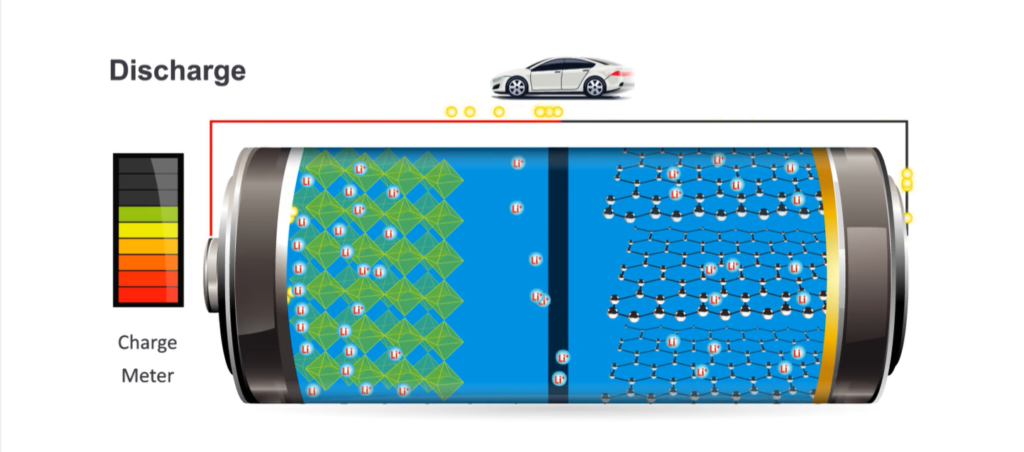
Source: U. S. Department of Energy
When providing electric current, the battery will be in discharging mode. In this process, the anode releases Li-ions to the cathode, resulting in a flow of electrons from one negative to the positive current collector.
While the battery is in charging mode, it stores electric current. In this process, the cathode releases Li-ions to the anode, resulting in a flow of electrons from the positive to the negative current collector.
Why are lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles?
There are several important reasons to choose Li-ion batteries over other batteries for electric vehicles. They are:
- High Energy Density
- High Power Density
- Long Cycle Life
- Low Self-Discharge
- Fast Charging
- Wide Operating Temperature Range
- Environmentally Friendly
Are lithium-ion batteries safe?
As long as there are no flaws and the batteries are not harmed, they are usually safe and unlikely to fail.
Li-ion batteries & the devices that have them shouldn’t go in the garbage or recycling bins. They can cause fires during transport or at landfills & recyclers. For proper disposal, call us.
Are lithium-ion batteries rechargeable?
Yes, a Li-ion battery is a rechargeable battery.
Rechargeability is undoubtedly a distinguishing feature of lithium-ion batteries and a major benefit over non-rechargeable substitutes such as alkaline batteries.
How to charge a lithium-ion battery?
Plug your EV into a compatible charging station, authenticate if required and monitor the charging progress. Set charging parameters if applicable and disconnect once your EV reaches the desired charge level.
Don’t charge to 100% every time. Frequent full charges can stress the battery. Aim for 80-90% for daily use.
Follow the manufacturer’s guide for charging your specific EV model.
How to dispose of a lithium-ion battery?
To ensure the proper disposal of used lithium-ion batteries, follow these easy three-step process mentioned below:
- Tape the Battery Terminals
- Pack Them in a Plastic/Cardboard Box
- Safer Battery Disposal
To know more, Click here.
What happens to used lithium-ion batteries?
| Disposal | What Happens? | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Proper | Recycling | > Healthy Earth > Compensation for Your Batteries > Sustainable Supply Chain |
| Improper | Landfill, Incineration or Littering | > Bad Health for Human > Bad health for Earth |
For the best possible outcome, call Renovar!
What happens when you overcharge a lithium-ion battery?
Overcharging generates excessive heat within the battery.
- This excessive heat can cause the battery to vent flammable gases, ignite or even explode.
- It can degrade the battery’s performance over time.
- Poses potential safety risks such as burns, property damage & even personal injury.
How to increase lithium-ion battery life?
Renovar’s tips to boost your battery life:
- Track Discharge: Monitor self-discharge to identify any unusual battery drain.
- Charge Smart: Opt for partial charges (80-90%) and use the proper charger.
- Go Easy on Fast Charging: Although convenient, frequent use can stress the battery.
Which battery is better: lithium-ion or polymer?
The word better doesn’t apply to this situation. It all depends on your needs:
- Choose Li-ion – For applications requiring maximum energy density and power, like power tools or EVs.
- Choose Li-po: For applications demanding flexible and lightweight batteries in devices like drones or cameras.
Are lithium-ion batteries environmentally friendly?
Offers environmental benefits over fossil fuels in terms of emissions and efficiency. Yet, concerns arise across their lifecycle, from mining to recycling and disposal.
Balancing these factors is key to sustainable energy choices.
Why are lithium-ion batteries so expensive?
Material expenses, complex manufacturing methods, safety and quality standards, severe regulations and ongoing research & development efforts influence the high cost of Li-ion batteries.
How long do lithium-ion batteries last?
Approximate lifespan Li-ion batteries based on application:
| Application | Battery Lifespan | |
| Charge/Discharge Cycles | Years | |
| Smartphone | 300-500 | 1-2 |
| Laptop | 500-800 | 2-4 |
| Electric vehicle | Around 3,000 | 8-10 |
| Power tool | 300-600 | 2-5 |
What could replace lithium-ion batteries?
The possible batteries that can possibly replace Li-ion batteries in future are given below:
- Sodium-ion batteries
- Magnesium batteries
- Lithium-sulfur batteries
- Solid-state batteries
They are currently under research and development. The future is yet to come. To know more, click here.
FAQs
Nah…Just Kidding!
Your Question Probably: Is This Blog Over?
Our answer is, It’s over for now! 😀


